The Lost Barrier Islands of Georgia
Anthony (Tony) Martin

The Georgia coast is well known for its historic role in the development of modern ecology, starting in the 1950s and ongoing today. But what about geologists? Fortunately, they were not long behind the ecologists, starting their research projects on Sapelo Island and other Georgia barrier islands in the early 1960s. Indeed, through that seminal work and investigations afterwards, these islands are currently renown for the insights they bestowed on our understanding of sedimentary geology.
Why would geologists be attracted to these islands made of shifting sand and mud that were nearly devoid of anything resembling a rock? Before sedimentary rocks can be made, sediments are needed, and those sediments must get deposited before solidifying into rock. Hence these geologists were interested in learning how the modern sands and muds of the barrier islands were deposited, eroded, or otherwise moved in coastal environments, a dynamism that can be watched and studied every day along any Georgia shoreline. The products of such sediment movement and deposition are sedimentary structures, which are either formed from physical processes - such as wind, waves, or tides - or biological processes, such as burrowing. Hence sedimentary structures can be classified as either physical or biogenic, respectively.
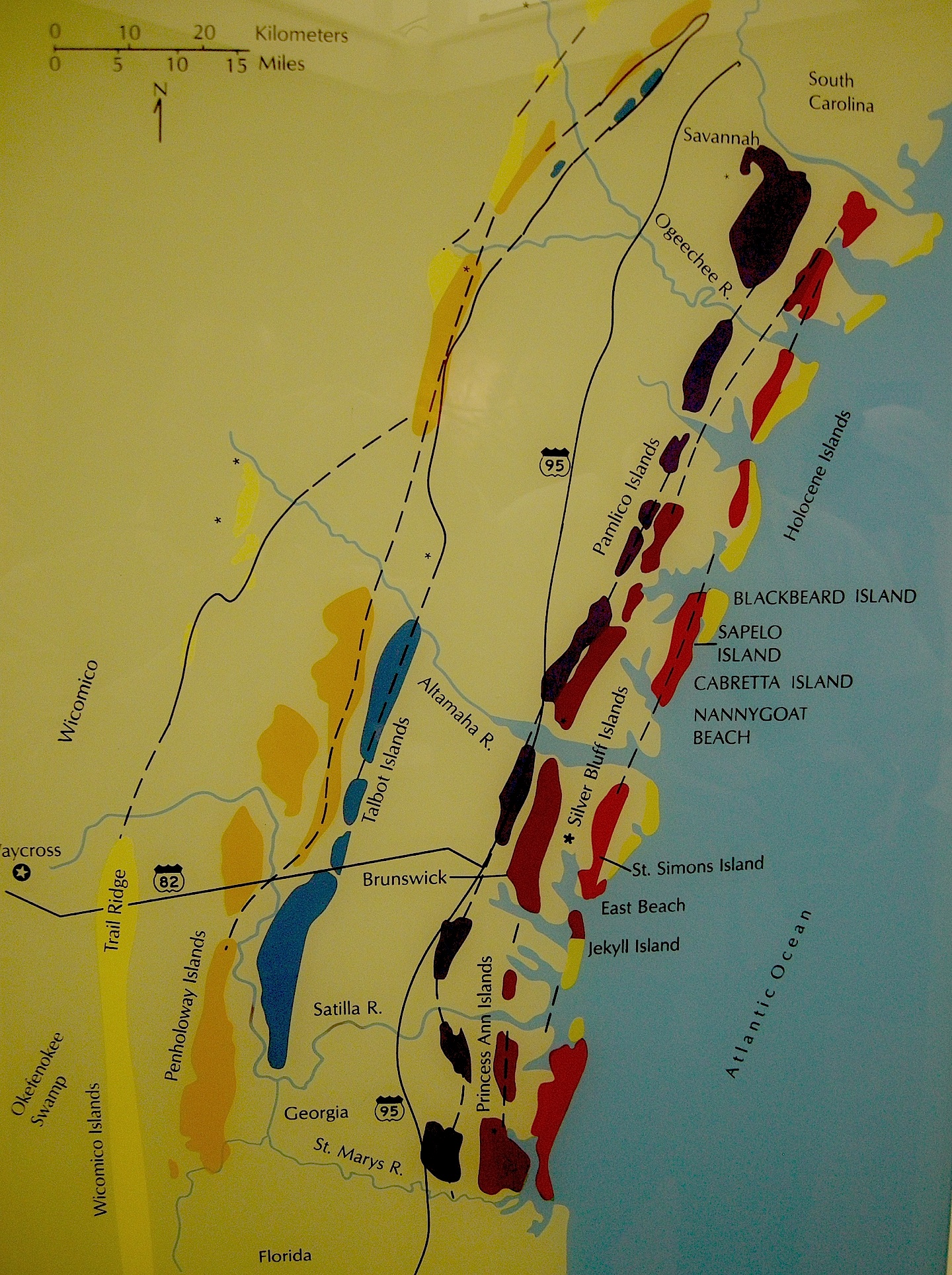
Through this integrated approach, they successfully showed that the long, linear sand ridges in on the coastal plain of southeastern Georgia were actually former dunes and beaches of ancient barrier islands.
Geologists who studied the Georgia barrier islands in the 1960s were among the first people in North America to apply what they observed in modern environments to ancient sedimentary deposits, and like the ecologists, they did it in Georgia. For example, in 1964, a few of these geologists - John H. Hoyt, Robert J. Weimer, and V.J. ("Jim") Henry - used a combination of: (1) geology, which involved looking at physical sedimentary structures and the sediments themselves; (2) modern traces made by coastal Georgia animals; and (3) Pleistocene trace fossils.
Through this integrated approach, they successfully showed that the long, linear sand ridges in on the coastal plain of southeastern Georgia were actually former dunes and beaches of ancient barrier islands. These sand ridges, which are barely discernible rises on a mostly flat coastal plain, are southwest-northeast trending and more-or-less parallel to the present Georgia shoreline. Remarkably, these ridges denote the positions of sea-level highs during the last few million years on the Georgia coastal plain. The geologists applied Native American and colonial names to each of these island systems - Wicomico, Penholoway, Talbot, Pamlico, Princess Anne, and Silver Bluff - with the most inland system reflecting the highest sea level.
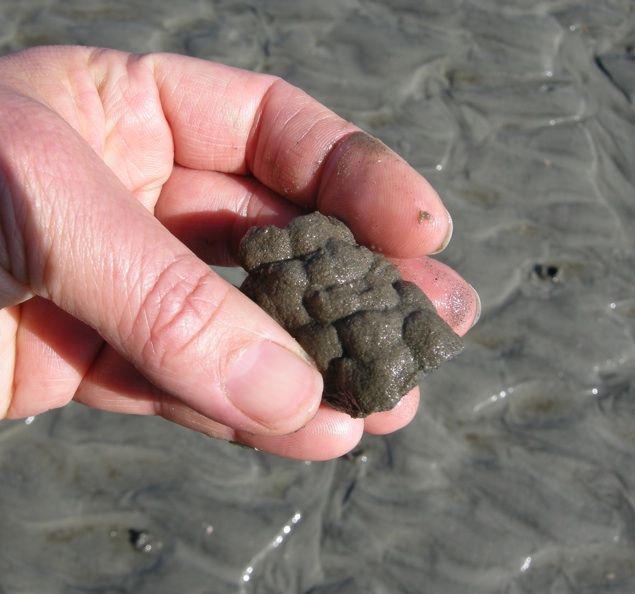
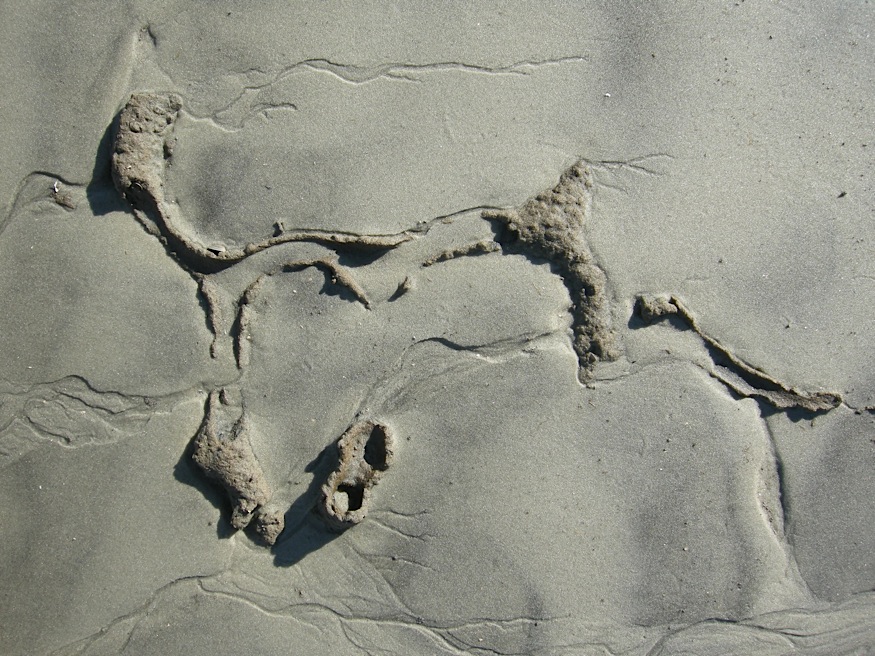
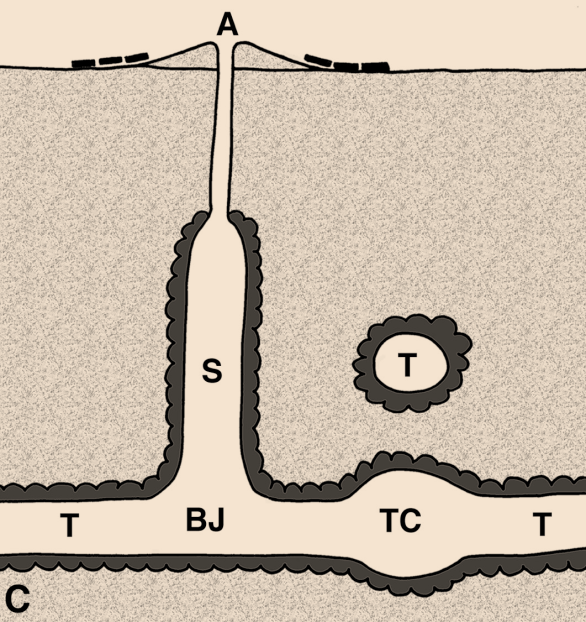
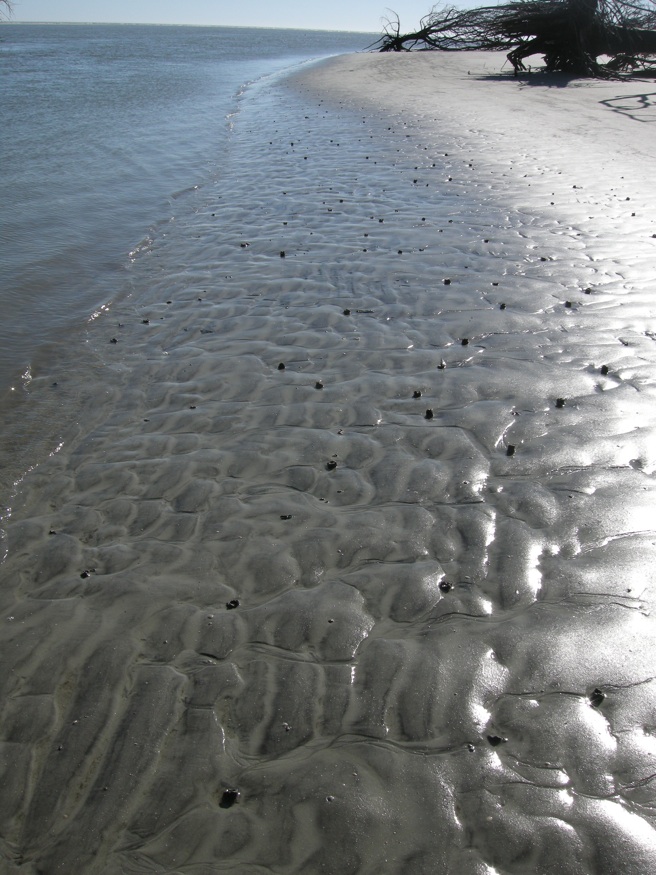
So how did these geologists figure out that a bunch of sand hills were actually lost barrier islands? And what does this all of this have to do with traces and trace fossils? The geologists first observed modern traces on Georgia shorelines that were burrows made by ghost shrimp, also known by biologists as callianassid shrimp. On a sandy beach surface, the tops of these burrows look like tiny shield volcanoes, and a burrow occupied by a ghost shrimp will complete that allusion by "erupting" water and fecal pellets through a narrow aperture.
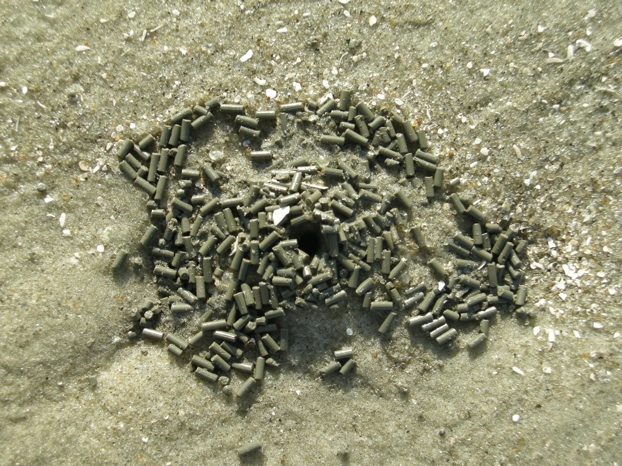


Just below the beach surface, these interior shafts widen considerably, making these burrows look more like wine bottles than volcanoes. This widening accommodates the ghost shrimp, which moves up and down the shaft to irrigate its burrow by pumping out its unwanted feces (understandable, that) and circulating oxygenated water into the burrow. Balls of muddy sand reinforce the burrow walls like bricks in a house, stuck together by shrimp spit, and the burrow interior is lined with a smooth wall of packed mud.
Amazingly, these shafts descend vertically far below the beach, as much as 2-3 meters (6.5-10 feet) deep. Here they turn horizontal, oblique, and vertical, and tunnels intersect, branch, and otherwise look like a complex tangle of piping, perhaps reminding baby-boomers of "jungle gyms" that they used to enjoy as children.
This is when geologists started realizing that the Georgia barrier islands were made of both Pleistocene and modern sediments as amalgams of two shorelines, and hence unlike any other known barrier islands in the world.
Ghost-shrimp burrows are definitely restricted to the shallow intertidal and subtidal environments of the Georgia coast, and their openings are visible at low tide on nearly every Georgia beach. Hence if you found similar burrows in the geologic record, you could reasonably infer that the sediments containing them were close to an ancient shoreline.
Before doing field work in the Georgia coastal plain, the geologists probably suspected that the sandy ridges there were associated with former shorelines. So with such a hypothesis in mind, they must have gratified to find fossil burrows preserved in the ancient sand deposits that matched the modern ghost-shrimp burrows they had seen on the Georgia coast. They also found these fossil burrows in Pleistocene-age deposits on the western side of Sapelo Island, which helped them to know where the shoreline was located about 40,000 years ago with respect to the present-day one. This is about the same time that geologists began realizing the Georgia barrier islands were made of both Pleistocene and modern sediments as amalgams of two shorelines. This made the Georgia islands special, unlike nearly every other known barrier island systems in the world.
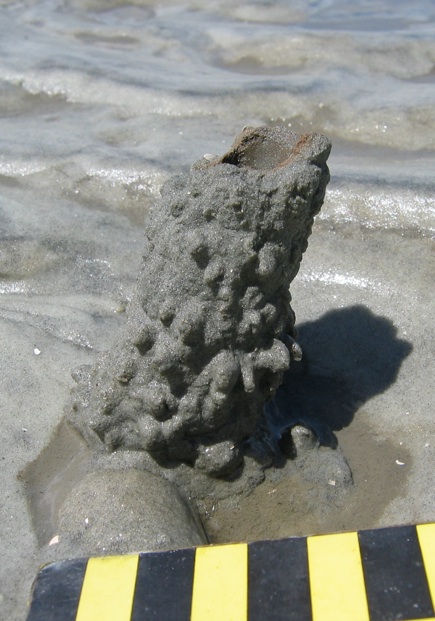
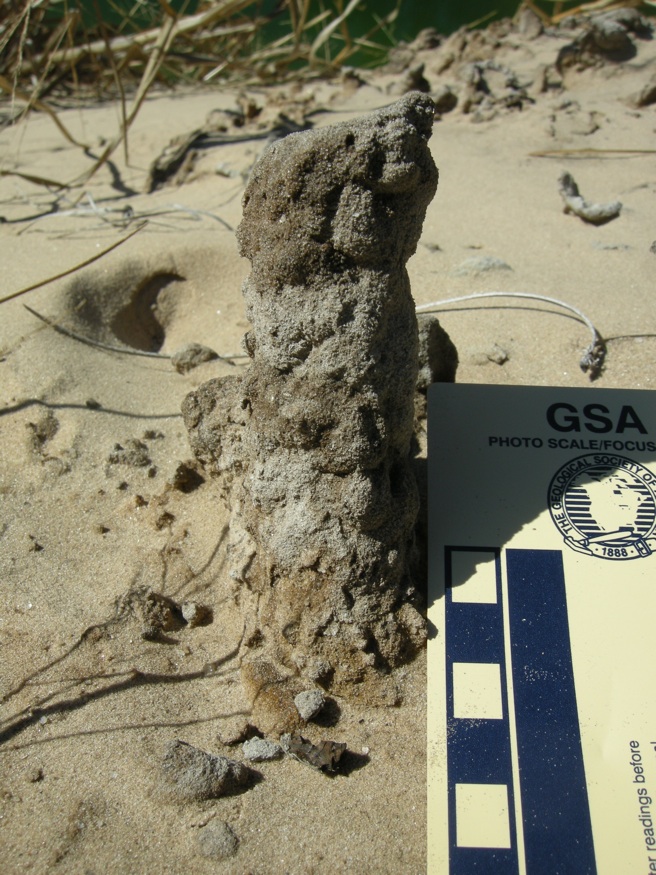


Geology and ecology combined further later in the 1960s, when paleontologists who also were well trained in biology began looking at how organisms - such as ghost shrimp, fiddler crabs, ghost crabs, mussels, and many other animals - actually change coastal sediments through their behavior and traces. So were these scientists considered geologists, biologists, or ecologists? They were actually greater than the sum of their parts: they were ichnologists. And what they found through their studies of modern traces on the Georgia barrier islands made these places even more scientifically famous, becoming recognized worldwide as among the best for comparing modern traces with trace fossils.
Anthony (Tony) Martin is a paleontologist and geologist who specializes in ichnology, the study of modern and ancient traces caused by animal behavior, such as tracks, trails, burrows, and nests. He is a Professor of Practice in the Department of Environmental Sciences at Emory University, where he has been for 25 years. At Emory, he teaches a variety of courses in paleontology, geology, and the environmental sciences on campus and in field courses, including study-abroad programs.
Further Reading
Hoyt, J.H., and Hails, J.R. 1967. Pleistocene shoreline sediments in coastal Georgia: deposition and modification. Science, 155: 1541-1543.
Hoyt, J.H., Weimer, R.J., and Henry, V.J., Jr. 1964. Late Pleistocene and recent sedimentation on the central Georgia coast, U.S.A. In van Straaten, L.M.J.U. (editor), Deltaic and Shallow Marine Deposits, Developments in Sedimentology I. Elsevier, Amsterdam: 170-176.
Martin, A.J. 2013. Life Traces of the Georgia Coast: Revealing the Unseen Lives of Plants and Animals. Indiana University Press, Bloomington (Indiana): 692 p.
Weimer, R.J., and Hoyt, J.H. 1964. Burrows of Callianassa major Say, geologic indicators of littoral and shallow neritic environments. Journal of Paleontology, 38: 761-767.